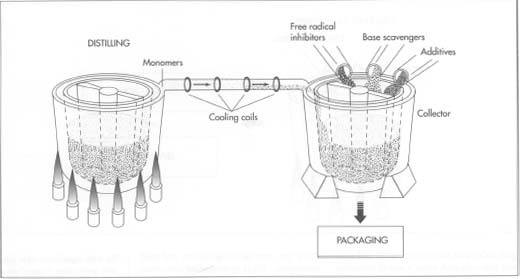
Introduction to Adhesive Manufacturing Process
Adhesive manufacturing process involves the production of various types of adhesives, both synthetic and natural, using specific methods and components. In the synthetic adhesive production process, chemical reactions play a vital role in creating the desired adhesive properties. Natural adhesives, on the other hand, are extracted from organic sources using different methods. Additives are often used in adhesive formulation to enhance performance and functionality. The curing process is crucial in adhesive manufacturing, as it determines the final strength and durability of the adhesive. Adhesives find applications in various industries and have both positive and negative environmental impacts.
Adhesive Industry Overview
The adhesive industry is a diverse and dynamic sector that plays a crucial role in various industries. Adhesive manufacturers produce a wide range of adhesives, both synthetic and natural, to meet the needs of different applications. These adhesives are used in industries such as automotive, construction, packaging, and electronics. With advancements in technology and increasing demand for sustainable solutions, the adhesive industry is continuously evolving. Manufacturers strive to develop innovative products with improved bonding strength, durability, and eco-friendly properties. Adhesive industry professionals stay up-to-date with market trends and collaborate with customers to provide customized adhesive solutions. The industry’s focus on research and development ensures the production of high-quality adhesives that meet the specific needs of various industries.
Basic Components of Adhesives
Adhesives are composed of three basic components: the resin, which provides adhesion and bonding properties; the filler, which enhances strength and stability; and the solvent or water, which serves as a carrier for the adhesive. Resins can be synthetic or natural, with each type offering different characteristics and performance. Fillers can include materials such as glass fibers or silica particles. Solvents or water are used to dissolve or disperse the resin and facilitate application. The proportions and specific components used in adhesives vary depending on the desired properties and application requirements. Manufacturers carefully formulate adhesives to ensure optimal bonding strength, flexibility, and overall performance.
Synthetic Adhesive Production
Synthetic adhesive production involves a complex manufacturing process that combines various chemicals and ingredients to create adhesives with specific properties. The process typically includes steps such as polymerization, blending, and curing. Polymerization is the reaction that forms the resin, which is then blended with fillers, solvents, and additives to achieve the desired adhesive properties. The mixture is then cured through processes such as heat, UV light, or moisture to ensure proper bonding and strength. The specific steps and methods used in synthetic adhesive production can vary depending on the type of adhesive being manufactured.
Synthetic Adhesive Manufacturing Process
Synthetic adhesive manufacturing involves a series of steps to produce adhesives with specific properties. The process starts with the polymerization reaction to form the resin, which is then blended with fillers, solvents, and additives. This mixture is then cured using methods such as heat, UV light, or moisture. The curing process ensures proper bonding and strength. The specific steps and methods used in synthetic adhesive production can vary depending on the type of adhesive being manufactured.
Chemical Reactions in Synthetic Adhesive Production
Chemical reactions play a crucial role in synthetic adhesive production, as they are responsible for the polymerization process that forms the adhesive resin. This polymerization reaction occurs when the monomers in the resin mixture react and bond together, creating a long-chain polymer. The type of monomers used and the reaction conditions can be tailored to achieve desired adhesive properties such as flexibility, strength, and adhesion. Additionally, crosslinking reactions may occur during curing to further enhance the adhesive’s performance. Overall, these chemical reactions are essential in creating synthetic adhesives with specific characteristics to meet various industrial and consumer needs.
Natural Adhesive Production
Natural adhesive production involves the extraction of adhesive materials from natural sources such as plants, animals, or minerals. The process typically begins with the collection of raw materials, which are then processed to release the adhesive substances. Extraction methods may include boiling, grinding, or fermentation. Once the adhesive material is obtained, it can be further refined and processed to improve its adhesive properties. Natural adhesives have different properties compared to synthetic adhesives, including lower toxicity and biodegradability. They are commonly used in applications such as woodworking, papermaking, and crafts. The production of natural adhesives provides sustainable alternatives to synthetic adhesives and supports eco-friendly practices.
Natural Adhesive Extraction Methods
Natural adhesive extraction methods involve various techniques for obtaining adhesive materials from natural sources. These methods include boiling, grinding, fermentation, or a combination of these processes. Boiling is commonly used to extract adhesive substances from plant materials by heating them in water and then collecting the resulting liquid. Grinding involves crushing the raw materials to release the adhesive components. Fermentation is another method used to extract adhesives, which involves allowing microorganisms to break down organic matter and produce adhesive substances. These extraction methods are essential in obtaining the adhesive materials needed for the production of natural adhesives.
Properties of Natural Adhesives
Properties of natural adhesives vary depending on the source material and extraction method. These adhesives are known for their biodegradability, low toxicity, and compatibility with organic substrates. They also offer good adhesion strength, flexibility, and resistance to moisture. Some natural adhesives, like animal-based adhesives, provide excellent heat resistance. However, natural adhesives may have limitations in terms of durability and long-term stability. It’s important to consider these properties when selecting and using natural adhesives for different applications.
Additives in Adhesive Formulation
Additives in adhesive formulation play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and versatility of adhesives. These additives are incorporated during the manufacturing process to improve properties such as adhesion strength, viscosity, flexibility, and durability. Some common additives used in adhesives include fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, and crosslinking agents. Fillers are added to increase the adhesive’s volume and improve its strength, while plasticizers enhance flexibility and reduce brittleness. Stabilizers help prevent degradation over time, and crosslinking agents promote curing reactions for stronger bonds. The careful selection and incorporation of additives in adhesive formulation contribute to the overall quality and effectiveness of the adhesive product.
Role of Additives in Adhesive Production
Role of Additives in Adhesive Production:
Additives play a crucial role in adhesive production by enhancing the performance and versatility of adhesives. They are incorporated during the manufacturing process to improve properties such as adhesion strength, viscosity, flexibility, and durability.
Fillers are added to increase the adhesive’s volume and strength, while plasticizers enhance flexibility and reduce brittleness. Stabilizers help prevent degradation over time, ensuring long-lasting adhesive performance. Crosslinking agents promote curing reactions, resulting in stronger bonds.
The careful selection and incorporation of additives contribute to the overall quality and effectiveness of the adhesive product, making it more suitable for various applications. By optimizing these additives, manufacturers can create adhesives that meet specific requirements and deliver superior performance in bonding different materials.
Common Additives Used in Adhesives
Common Additives Used in Adhesives:
Common additives used in adhesives include fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, and crosslinking agents. Fillers are added to increase volume and strength, while plasticizers enhance flexibility and reduce brittleness. Stabilizers prevent degradation over time, ensuring long-lasting performance. Crosslinking agents promote curing reactions, resulting in stronger bonds. These additives are carefully selected and incorporated during the manufacturing process to improve adhesive properties such as adhesion strength, viscosity, flexibility, and durability. By optimizing the use of these additives, manufacturers can create adhesives that meet specific requirements and deliver superior performance for bonding different materials.
Adhesive Curing Process
Adhesive Curing Process:
During the adhesive curing process, the adhesive undergoes a chemical or physical change that transforms it from a liquid or semi-liquid state to a solid state, creating a strong bond between the surfaces being joined. The curing process can be achieved through various methods such as heat, pressure, or exposure to ultraviolet light. Heat curing involves applying heat to accelerate the chemical reaction and promote crosslinking of adhesive components. Pressure curing applies pressure to enhance contact between adhesive and substrate, facilitating faster bonding. Ultraviolet (UV) curing utilizes UV light to initiate a photochemical reaction in UV-sensitive adhesives, resulting in rapid curing and strong adhesion. The choice of curing method depends on the type of adhesive and its intended application.
Curing Methods in Adhesive Manufacturing
Curing Methods in Adhesive Manufacturing:
Different curing methods are used in adhesive manufacturing to achieve optimal bond strength and durability. Heat curing involves applying controlled heat to accelerate the chemical reaction of the adhesive. Pressure curing applies pressure to enhance contact between the adhesive and substrate, resulting in faster bonding. UV curing utilizes ultraviolet light to initiate a photochemical reaction in UV-sensitive adhesives, leading to rapid curing and strong adhesion. Moisture curing relies on the presence of atmospheric moisture to trigger the adhesive’s chemical reaction. Each method has its benefits and is chosen based on the specific adhesive formulation and desired application requirements.
Impact of Curing on Adhesive Performance
Curing plays a crucial role in determining the performance of adhesives. It enhances bond strength, durability, and overall adhesive properties. Proper curing ensures that the adhesive fully polymerizes and forms strong molecular bonds with the substrate. Incomplete or improper curing can lead to weak bonds, reduced adhesion strength, and compromised performance. The curing process affects factors such as flexibility, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and moisture resistance of the adhesive. Adhesive manufacturers carefully select the appropriate curing method based on the adhesive formulation and desired application requirements. By understanding the impact of curing on adhesive performance, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and deliver high-quality adhesives for various industries and applications.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Adhesive manufacturing is a complex process that involves the production of synthetic and natural adhesives, the addition of additives to enhance adhesive properties, and the curing process to optimize adhesive performance. Understanding the basic components and chemical reactions involved in adhesive production is crucial for developing high-quality adhesives. Additives play a significant role in enhancing adhesive properties, such as viscosity, tackiness, and durability. The curing process ensures that the adhesive fully polymerizes and forms strong bonds with the substrate, resulting in improved bond strength and overall performance. By carefully controlling each step of the manufacturing process, manufacturers can produce adhesives that meet the specific needs of various industries and applications.
Uses and Applications of Adhesives
Adhesives are widely used in various industries and applications, making them an essential part of our daily lives. They are commonly used in construction for bonding materials like wood, metal, and plastic. Additionally, adhesives are crucial in the automotive industry for assembling parts and components. They also find extensive use in the packaging industry for sealing boxes and cartons. Adhesives are employed in the furniture industry for joining pieces together and in the electronics industry for bonding circuit boards and components. Moreover, adhesives are utilized in the medical field for wound closure and in the aerospace industry for aircraft assembly. The versatility and convenience of adhesives make them indispensable in numerous applications.
Environmental Impact of Adhesive Production
Adhesive production has a significant environmental impact, primarily due to the chemicals and materials used in the manufacturing process. The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production contributes to air pollution and can have adverse effects on human health. Additionally, the disposal of adhesive waste can contaminate soil and water sources, posing a threat to ecosystems. To mitigate these environmental impacts, adhesive manufacturers are adopting more sustainable practices. These include reducing VOC emissions, using renewable or bio-based materials, and implementing recycling and waste management programs. By prioritizing environmental considerations in adhesive production, the industry aims to minimize its ecological footprint and promote sustainability.