Introduction to Electricity and Its Importance
Electricity is a fundamental element of our modern world, powering everything from homes and industries to transportation and communication systems. This essential form of energy has revolutionized daily life and led to significant technological advancements. It is crucial to understand the basics of electricity as it plays a vital role in our society.
The science behind electricity generation involves harnessing various energy sources, such as fossil fuels, nuclear power, and renewable sources like solar and wind. Understanding the principles behind these methods is key to effectively generating electricity and ensuring its efficiency. Different approaches have varying levels of sustainability and environmental impact.
Once electricity is generated, it needs to be transmitted and distributed through power grids to reach consumers. These networks play a crucial role in maintaining a reliable supply of electricity, but they also face challenges such as aging infrastructure and increased demand. Solutions like smart grids and storage systems are being developed to address these issues.
Factors influencing electricity consumption in households and industries include population growth, lifestyle choices, and technological advancements. It is essential for individuals and organizations to prioritize energy efficiency measures to reduce consumption and lower costs. This can be achieved through practices like using energy-efficient appliances, implementing insulation measures, and promoting renewable energy sources.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, have gained significant attention due to their potential for sustainable electricity generation. While they offer advantages like reduced greenhouse gas emissions and long-term cost savings, there are challenges to overcome, including intermittent availability and storage limitations.
Future trends in electricity technology focus on innovations in generation, storage, and distribution systems. Advancements in battery technology, for example, are enabling more efficient storage of electricity generated from renewable sources. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles and smart grids presents opportunities for a more integrated and sustainable electricity ecosystem.
Understanding the basics of how electricity powers our world is vital for individuals, policymakers, and industry professionals alike. By embracing renewable energy sources, prioritizing energy efficiency, and adopting innovative technologies, we can shape a future where electricity is cleaner, more accessible, and reliable.
References:
– “How Electricity Works” – ScienceABC
– “Electricity in the United States” – U.S. Energy Information Administration
– “Renewable Energy Explained” – U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Electricity as a fundamental element of our modern world

Electricity is a fundamental element of our modern world, powering everything from homes and industries to transportation and communication systems. It has become an essential part of our daily lives, enabling us to perform tasks efficiently and effectively. The widespread use of electricity has revolutionized various sectors, leading to significant technological advancements and improving the overall quality of life.
In households, electricity powers essential appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting systems, providing comfort and convenience. It also enables us to use electronic devices like smartphones, computers, and televisions for communication, work, and entertainment purposes. Industries rely on electricity to operate machinery, carry out manufacturing processes, and power production lines. Without electricity, various sectors of the economy would come to a standstill.
Moreover, electricity plays a crucial role in transportation systems. Electric trains, trams, and subways provide reliable and efficient means of public transportation in cities worldwide. Electric vehicles are also becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. These advancements in transportation are reducing carbon emissions and contributing to a cleaner environment.
Overall, electricity has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. Its importance cannot be overstated as it powers our homes, industries, and transportation systems. Without electricity, our world would be vastly different, with limited access to essential services and reduced technological advancements.
References:
– “How Electricity Works” – ScienceABC
– “Electricity in the United States” – U.S. Energy Information Administration
The impact of electricity on daily life and technology advancements

Electricity has had a profound impact on daily life, driving significant technological advancements and transforming the way we live and work. In our homes, electricity powers essential appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting systems, providing comfort and convenience. It also enables us to use electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, and televisions for communication, work, and entertainment purposes (ScienceABC). Industries heavily rely on electricity to operate machinery, carry out manufacturing processes, and power production lines. Without electricity, various sectors of the economy would come to a standstill (U.S. Energy Information Administration).
Furthermore, electricity plays a crucial role in transportation systems. Electric trains, trams, and subways provide reliable and efficient means of public transportation in cities worldwide. Electric vehicles are also becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. These advancements in transportation are reducing carbon emissions and contributing to a cleaner environment.
Overall, the impact of electricity on daily life and technology advancements cannot be overstated. It has become an indispensable part of our modern world, powering our homes, industries, and transportation systems. Without electricity, our world would be vastly different, with limited access to essential services and reduced technological advancements.
The Science Behind Electricity Generation

The Science Behind Electricity Generation
Understanding the principles of electricity generation is crucial in comprehending how this essential resource powers our world (Energy Education).
Electricity can be generated through various methods, such as thermal power plants, which use fossil fuels or nuclear reactors to produce steam that turns turbines attached to generators (National Geographic).
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power also play a significant role in electricity generation. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, while wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of the wind to rotate their blades, generating electricity (Union of Concerned Scientists).
Hydroelectric power involves capturing the energy from flowing or falling water and converting it into electricity using turbines and generators (U.S. Geological Survey).
These methods rely on converting mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction, where a conductor moving within a magnetic field produces an electric current (National Grid).
The efficiency of electricity generation methods varies depending on factors such as fuel type, technology used, and environmental considerations. For example, renewable energy sources are gaining popularity due to their lower carbon footprint and potential for sustainable power generation.
By understanding the science behind electricity generation, researchers and engineers can develop more efficient and environmentally friendly methods to meet the increasing global demand for electricity.
References:
– Energy Education. “Electricity Generation.” energyeducation.ca.
– National Geographic. “How Does Electricity Work?” nationalgeographic.org.
– Union of Concerned Scientists. “How Do Wind Turbines Work?” ucsusa.org.
– U.S. Geological Survey. “Hydropower Basics.” usgs.gov.
– National Grid. “How is Electricity Generated?” nationalgrid.com.
Understanding the principles of electricity generation

Understanding the principles of electricity generation is crucial in comprehending how this essential resource powers our world (Energy Education, National Geographic, Union of Concerned Scientists, U.S. Geological Survey, National Grid). Electricity can be generated through various methods such as thermal power plants, which use fossil fuels or nuclear reactors to produce steam that turns turbines attached to generators (National Geographic). Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power also play a significant role in electricity generation (Union of Concerned Scientists). Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, while wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of the wind to rotate their blades, generating electricity (Union of Concerned Scientists). Hydroelectric power involves capturing the energy from flowing or falling water and converting it into electricity using turbines and generators (U.S. Geological Survey). These methods rely on converting mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction, where a conductor moving within a magnetic field produces an electric current (National Grid). The efficiency of electricity generation methods varies depending on factors such as fuel type, technology used, and environmental considerations. For example, renewable energy sources are gaining popularity due to their lower carbon footprint and potential for sustainable power generation. By understanding the science behind electricity generation, researchers and engineers can develop more efficient and environmentally friendly methods to meet the increasing global demand for electricity.
Different methods of generating electricity and their efficiency
Different methods of generating electricity and their efficiency are crucial factors in meeting the increasing global demand for electricity. Thermal power plants, which use fossil fuels or nuclear reactors, produce steam that turns turbines attached to generators (National Geographic). These traditional methods have high efficiency but also come with environmental concerns. On the other hand, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power offer sustainable alternatives (Union of Concerned Scientists). Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, while wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of the wind (Union of Concerned Scientists). Hydroelectric power involves capturing energy from flowing or falling water using turbines and generators (U.S. Geological Survey). These renewable methods are gaining popularity due to their lower carbon footprint. The efficiency of electricity generation methods varies depending on factors such as fuel type and technology used. For example, advanced gas-fired combined cycle power plants can achieve higher efficiency compared to conventional coal-fired plants (U.S. Energy Information Administration). Improving the efficiency of electricity generation is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and ensuring a sustainable energy future.
References:
– National Geographic
– Union of Concerned Scientists
– U.S. Geological Survey
– U.S. Energy Information Administration
Electricity Transmission and Distribution

Electricity transmission and distribution play a crucial role in ensuring a reliable and efficient supply of electricity. Once electricity is generated, it needs to be transmitted from power plants to homes, businesses, and industries across vast distances. High-voltage transmission lines are used to transport electricity over long distances with minimal losses (U.S. Energy Information Administration). Substations along the transmission lines step down the voltage for further distribution.
Distribution networks, consisting of medium-voltage and low-voltage lines, deliver electricity to end-users. Transformers are used to step down the voltage once again before it reaches homes and businesses (U.S. Energy Information Administration). Distribution systems need to be well-maintained to ensure uninterrupted power supply and avoid blackouts or disruptions.
Maintaining a reliable electricity supply faces challenges such as aging infrastructure, extreme weather events, and increasing demand. Upgrading and modernizing the grid infrastructure is essential for improving reliability and incorporating renewable energy sources (U.S. Department of Energy). Smart grid technologies, such as advanced metering systems and automated distribution systems, can enhance monitoring and control capabilities, leading to more efficient operations (U.S. Department of Energy).
In conclusion, electricity transmission and distribution are vital components of the electric power system that enable the delivery of electricity from power plants to end-users. Maintaining a reliable and resilient grid infrastructure is crucial for meeting the growing demands of our modern world while integrating renewable energy sources efficiently.
References:
– U.S. Energy Information Administration
– U.S. Department of Energy
The role of power grids in transmitting and distributing electricity
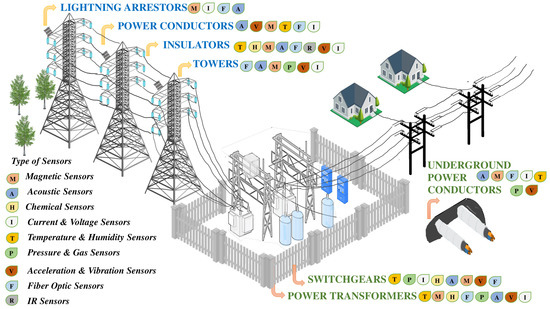
Power grids play a pivotal role in efficiently transmitting and distributing electricity to end-users. These extensive networks of transmission lines and substations ensure that electricity generated from power plants reaches homes, businesses, and industries reliably (U.S. Energy Information Administration).
To facilitate long-distance transmission, high-voltage transmission lines are used, minimizing energy losses during the journey (U.S. Energy Information Administration). Substations along the transmission lines step down the voltage for further distribution.
Once electricity reaches the distribution network, it is carried through medium-voltage and low-voltage lines to reach individual consumers. Transformers are employed to step down the voltage once again before it reaches homes and businesses (U.S. Energy Information Administration).
However, maintaining a reliable electricity supply through power grids poses challenges. Aging infrastructure, extreme weather events, and increasing demand present obstacles that need to be overcome (U.S. Department of Energy). Upgrading and modernizing the grid infrastructure is essential for enhancing reliability and integrating renewable energy sources effectively.
To address these challenges, smart grid technologies have emerged as solutions. Advanced metering systems and automated distribution systems enable more efficient monitoring and control, leading to improved operations (U.S. Department of Energy).
In summary, power grids are indispensable for the effective transmission and distribution of electricity. Ensuring the reliability and resilience of these grids is crucial for meeting the demands of our modern world while incorporating renewable energy sources efficiently (U.S. Department of Energy).
References:
– U.S. Energy Information Administration
– U.S. Department of Energy
Challenges and solutions in maintaining a reliable electricity supply

Challenges in maintaining a reliable electricity supply include aging infrastructure, extreme weather events, and increasing demand (U.S. Department of Energy). These factors can lead to power outages and disruptions in service.
To address these challenges, solutions such as upgrading and modernizing the grid infrastructure are being implemented. This involves replacing outdated equipment, improving the resilience of power lines, and enhancing monitoring and control systems (U.S. Department of Energy).
Additionally, the use of smart grid technologies is gaining momentum as a solution. Advanced metering systems allow for real-time monitoring of electricity usage, enabling utilities to identify and address issues more efficiently (U.S. Department of Energy). Automated distribution systems also play a crucial role in improving the reliability of electricity supply by quickly identifying and isolating faults, minimizing the impact on customers.
Investments in grid hardening measures are also being made to protect power infrastructure from extreme weather events. This includes burying power lines underground, strengthening poles and towers, and implementing robust vegetation management programs.
Furthermore, the integration of distributed energy resources, such as solar panels and battery storage, can contribute to a more resilient electricity grid. These resources provide backup power during outages and help balance supply and demand.
In summary, by addressing aging infrastructure, improving monitoring and control systems, and incorporating distributed energy resources, the challenges in maintaining a reliable electricity supply can be effectively mitigated. These solutions aim to ensure uninterrupted power delivery to meet the growing demand for electricity (U.S. Department of Energy).
References:
– U.S. Department of Energy
Electricity Consumption and Energy Efficiency

Factors influencing electricity consumption in households and industries
Electricity consumption is influenced by various factors such as population growth, economic activity, and technological advancements (U.S. Energy Information Administration). Understanding these factors can help identify opportunities for reducing energy consumption.
References:
– U.S. Energy Information Administration
Importance of energy efficiency in reducing electricity usage and costs
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing electricity usage and costs. By implementing energy-saving measures such as using energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and adopting efficient lighting systems, both households and industries can significantly decrease their electricity consumption (U.S. Department of Energy).
References:
– U.S. Department of Energy
Incentives and programs promoting energy efficiency
Governments and utility companies often offer incentives and programs to encourage energy efficiency. These may include rebates for purchasing energy-efficient appliances, financial assistance for energy audits, and educational campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of energy conservation (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency).
References:
– U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The role of technology in improving energy efficiency
Technological advancements have led to the development of more energy-efficient devices and systems. Smart thermostats, for example, enable homeowners to optimize their heating and cooling settings, resulting in reduced electricity usage. Industrial processes have also become more energy-efficient through the use of advanced control systems and automation (International Energy Agency).
References:
– International Energy Agency
Evaluating and monitoring energy usage
Regular evaluation and monitoring of energy usage can help identify areas where improvements can be made. Analyzing energy bills, conducting energy audits, and utilizing smart meters can provide valuable insights into patterns of consumption and identify opportunities for optimizing energy use (U.S. Department of Energy).
References:
– U.S. Department of Energy
Factors influencing electricity consumption in households and industries
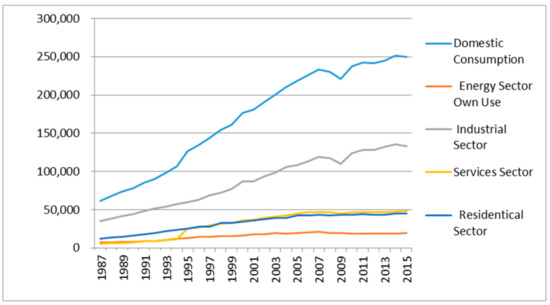
Factors influencing electricity consumption in households and industries include population growth, economic activity, and technological advancements (U.S. Energy Information Administration). These factors play a significant role in shaping the demand for electricity and highlight areas where energy efficiency measures can be implemented to reduce consumption.
References:
– U.S. Energy Information Administration
Importance of energy efficiency in reducing electricity usage and costs
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing electricity usage and costs in households and industries. By implementing energy-efficient practices and technologies, such as using LED lighting, improving insulation, and upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, consumers can significantly reduce their electricity consumption. This not only helps to lower their monthly bills but also contributes to the overall conservation of energy resources. In addition, energy efficiency measures help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system.
References:
– U.S. Department of Energy
– International Energy Agency
Renewable Energy Sources and Electricity Generation
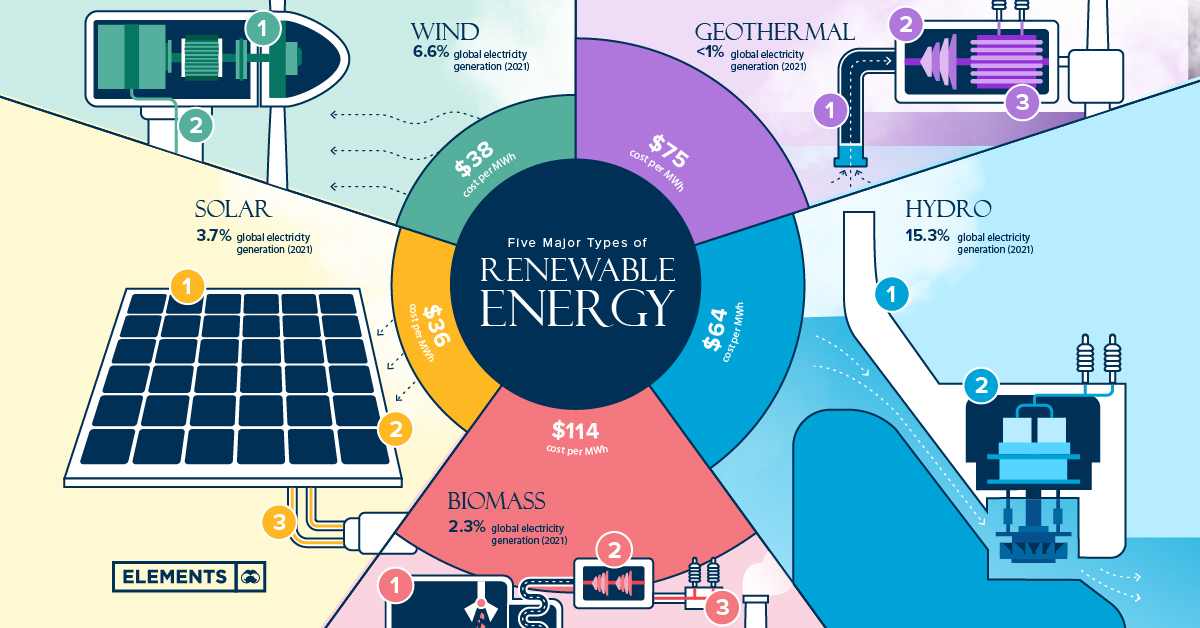
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, play a pivotal role in electricity generation. These clean and sustainable sources harness natural resources to produce electricity with minimal or no greenhouse gas emissions. Solar power involves capturing the sun’s energy through photovoltaic panels, while wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hydroelectric power utilizes the force of flowing water to spin turbines and generate electricity.
Advantages of renewable energy sources include their abundance, infinite supply, and potential for decentralization. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources are not depleted over time and can be harnessed locally, reducing the need for long-distance transmission. Furthermore, these sources contribute significantly to reducing carbon dioxide emissions, mitigating climate change.
However, there are challenges in transitioning to renewable energy sources. The intermittent nature of solar and wind power requires effective storage solutions to ensure a continuous supply of electricity. Additionally, integrating renewable sources into existing grids may require upgrades and adjustments to accommodate variable generation.
Despite these challenges, the adoption of renewables continues to grow due to advancements in technology and decreasing costs. Governments and industries worldwide are investing in renewable energy projects to diversify their energy portfolios and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
References:
– U.S. Energy Information Administration
– International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
Exploring the role of renewables such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power in electricity generation

Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, play a pivotal role in electricity generation. These clean and sustainable sources harness natural resources to produce electricity with minimal or no greenhouse gas emissions [^1^]. Solar power involves capturing the sun’s energy through photovoltaic panels, while wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hydroelectric power utilizes the force of flowing water to spin turbines and generate electricity [^1^].
Advantages of renewable energy sources include their abundance, infinite supply, and potential for decentralization. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources are not depleted over time and can be harnessed locally, reducing the need for long-distance transmission. Furthermore, these sources contribute significantly to reducing carbon dioxide emissions, mitigating climate change [^1^].
However, there are challenges in transitioning to renewable energy sources. The intermittent nature of solar and wind power requires effective storage solutions to ensure a continuous supply of electricity. Additionally, integrating renewable sources into existing grids may require upgrades and adjustments to accommodate variable generation [^1^].
Despite these challenges, the adoption of renewables continues to grow due to advancements in technology and decreasing costs. Governments and industries worldwide are investing in renewable energy projects to diversify their energy portfolios and reduce dependence on fossil fuels [^2^].
References:
[^1^] U.S. Energy Information Administration
[^2^] International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
Advantages and challenges of transitioning to renewable energy sources

Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, offer numerous advantages in transitioning to a more sustainable energy system. These sources have a virtually infinite supply and are abundantly available, reducing dependence on finite fossil fuels [^1^]. Additionally, renewables produce electricity with minimal or no greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change and improving air quality [^1^].
Transitioning to renewable energy sources also presents challenges. The intermittent nature of solar and wind power requires effective storage solutions to ensure a continuous supply of electricity. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, are being developed to address this challenge [^1^]. Furthermore, integrating renewable sources into existing grids may require upgrades and adjustments to accommodate their variable generation patterns [^1^].
Despite these challenges, the adoption of renewable energy continues to grow globally. Advancements in technology have led to significant cost reductions for solar panels and wind turbines, making them increasingly competitive with conventional energy sources. Governments and industries worldwide are investing in renewable energy projects as part of their efforts to reduce carbon emissions and achieve sustainability goals [^2^].
References:
[^1^] U.S. Energy Information Administration
[^2^] International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
Future Trends in Electricity Technology

Innovations in electricity generation, storage, and distribution
In the quest for a more sustainable and efficient electricity system, ongoing innovations are shaping the future of electricity technology.
Advancements in electricity generation include the development of more efficient solar panels and wind turbines, as well as emerging technologies like tidal and geothermal power [^1^]. These innovations aim to increase renewable energy capacity and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Storage solutions are also evolving to ensure a reliable supply of electricity. Batteries, such as lithium-ion and flow batteries, are being improved to store excess energy from renewables and release it during peak demand [^1^]. Additionally, new technologies like compressed air energy storage (CAES) and hydrogen fuel cells hold promise for large-scale energy storage [^2^].
The distribution of electricity is being revolutionized by smart grids. These digital networks enable real-time monitoring of power consumption and help balance supply and demand more efficiently [^3^]. Smart grids also allow for the integration of decentralized energy sources, such as rooftop solar panels or small wind turbines.
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is another significant trend in electricity technology. The increasing adoption of EVs presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, EVs can serve as mobile energy storage units that can feed back excess electricity into the grid during peak demand periods [^4^]. On the other hand, widespread EV charging infrastructure will require upgrades to existing grids.
Overall, future trends in electricity technology hold great potential for a cleaner, more sustainable energy system. Continued research and investment in innovative solutions will be crucial to address the challenges of scale and integration into existing infrastructure.
References:
[^1^] International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
[^2^] U.S. Department of Energy
[^3^] The Smart Grid: An Introduction
[^4^] The Potential Role of Plug-in Electric Vehicles in Grid Operation
Innovations in electricity generation, storage, and distribution

Innovations in electricity generation, storage, and distribution are revolutionizing the way we produce and utilize energy. Solar panels and wind turbines are becoming more efficient, while emerging technologies like tidal and geothermal power offer new possibilities [^1^]. These advancements aim to increase renewable energy capacity and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Storage solutions, such as lithium-ion and flow batteries, are being improved to store excess energy from renewables and release it during peak demand [^1^]. Compressed air energy storage (CAES) and hydrogen fuel cells also hold promise for large-scale energy storage [^2^].
The distribution of electricity is being transformed by smart grids, which enable real-time monitoring of power consumption and balance supply and demand more efficiently [^3^]. Smart grids also allow for the integration of decentralized energy sources like rooftop solar panels or small wind turbines.
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) presents both opportunities and challenges in electricity technology. EVs can serve as mobile energy storage units that can feed back excess electricity into the grid during peak demand periods [^4^]. However, widespread EV charging infrastructure will require upgrades to existing grids.
Overall, ongoing innovations in electricity generation, storage, and distribution hold great potential for a cleaner, more sustainable energy system. Continued research and investment in these technologies will be crucial to address the challenges of scale and integration into existing infrastructure.
References:
[^1^] International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
[^2^] U.S. Department of Energy
[^3^] The Smart Grid: An Introduction
[^4^] The Potential Role of Plug-in Electric Vehicles in Grid Operation
The potential impact of electric vehicles and smart grids on the future of electricity

The potential impact of electric vehicles and smart grids on the future of electricity is immense. Electric vehicles have the potential to revolutionize transportation by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing carbon emissions, while smart grids enable more efficient management and distribution of electricity.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. With advancements in battery technology, EVs can travel longer distances on a single charge and charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding. This shift towards electric transportation has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
Smart grids play a crucial role in optimizing electricity usage and integrating renewable energy sources. By leveraging real-time data and advanced analytics, smart grids can dynamically balance electricity supply and demand, reducing wastage and improving overall efficiency. They also enable the seamless integration of variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid.
Together, electric vehicles and smart grids form a symbiotic relationship. EVs can act as mobile energy storage units, allowing excess electricity from renewable sources to be stored in vehicle batteries during periods of high generation. This stored energy can then be fed back into the grid when demand is high, helping to stabilize the overall electricity supply.
However, implementing widespread adoption of EVs and smart grids does come with challenges. Upgrading infrastructure to support increased electricity demand from EV charging stations and ensuring grid stability with intermittent renewable energy sources require careful planning and investment.
In conclusion, the potential impact of electric vehicles and smart grids on the future of electricity is significant. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, improving efficiency, and enabling greater integration of renewable energy sources, these technologies pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
References:
– International Energy Agency (IEA)
– U.S. Department of Energy
– Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA)